Many people wonder whether eye exercises can correct a lazy eye, especially when searching for non-surgical and non-invasive solutions for themselves or their children. Before exploring treatment options, it’s important to understand what lazy eye actually is.
Lazy eye, medically known as amblyopia, is a visual development condition in which one eye fails to achieve normal visual acuity even with glasses or contact lenses. If left untreated, it can lead to permanent vision impairment and, in severe cases, legal blindness.
Although amblyopia is most commonly treated in childhood, it can persist into adulthood. This has led to increased interest in lazy eye exercises, vision therapy for amblyopia, and structured rehabilitation programs for both children and adults.
This doctor-backed guide explains what eye exercises can and cannot do, who benefits most from them, and how supervised treatment leads to the best long-term outcomes.
Medical Disclaimer: Eye exercises and vision therapy should only be performed under the guidance of a qualified ophthalmologist or squint specialist. Self-treatment without proper diagnosis may delay effective care.
Table of Contents |
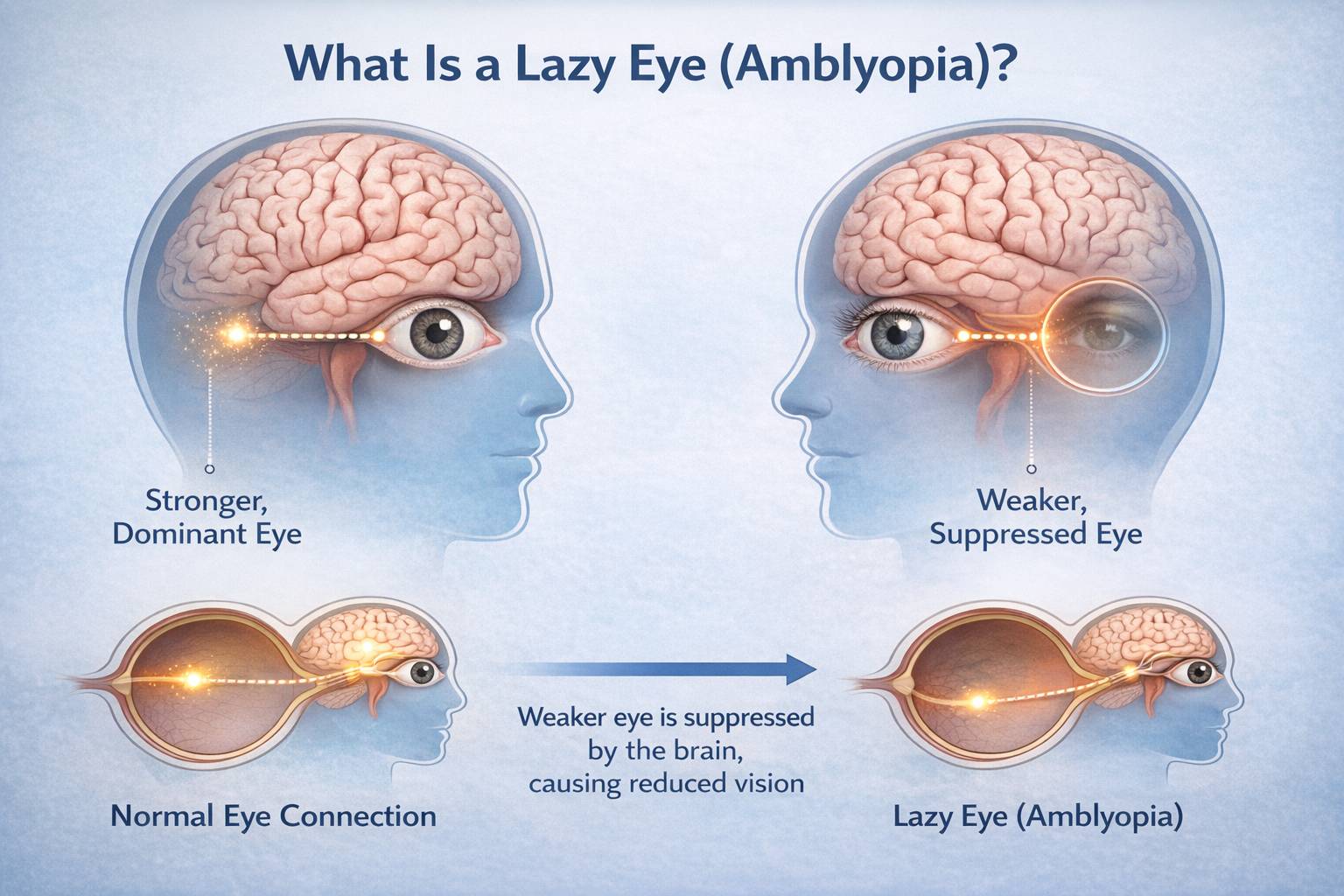
What Is a Lazy Eye (Amblyopia)?
Lazy eye (amblyopia) occurs when the brain favors one eye over the other, leading to reduced vision in the weaker eye. Importantly, amblyopia is not caused by a structural defect in the eye itself, it is a problem of visual processing in the brain.
The condition usually develops in early childhood, but without proper treatment, it can continue into adulthood. When intervention is delayed, the brain permanently suppresses signals from the weaker eye, making recovery more challenging later in life.
Understanding amblyopia is essential for parents seeking early treatment and for adults who believe nothing can be done because that belief is incorrect.
What Causes Lazy Eye?
Lazy eye can develop due to several reasons. They include:
1. Refractive Errors
The presence of large discrepancies between the eyes in visual processing, such as unequal nearsightedness, farsightedness, or astigmatism, creates bias and visual dominance-likelihood of the brain to preferentially select one eye.
2. Strabismus (Eye Misalignment)
Misalignment of one eye either by turning in, out, up or down causes the brain to ignore the misaligned eye in the absence of vision. This is to avoid the perception of double vision.
3. Deprivation Amblyopia
If the eye is obstructed in the early stages, as with congenital cataracts, severe lazy eye can result and go untreated. Regardless of the reason, early intervention and appropriate treatment, like amblyopia therapies, can achieve pronounced positive results.
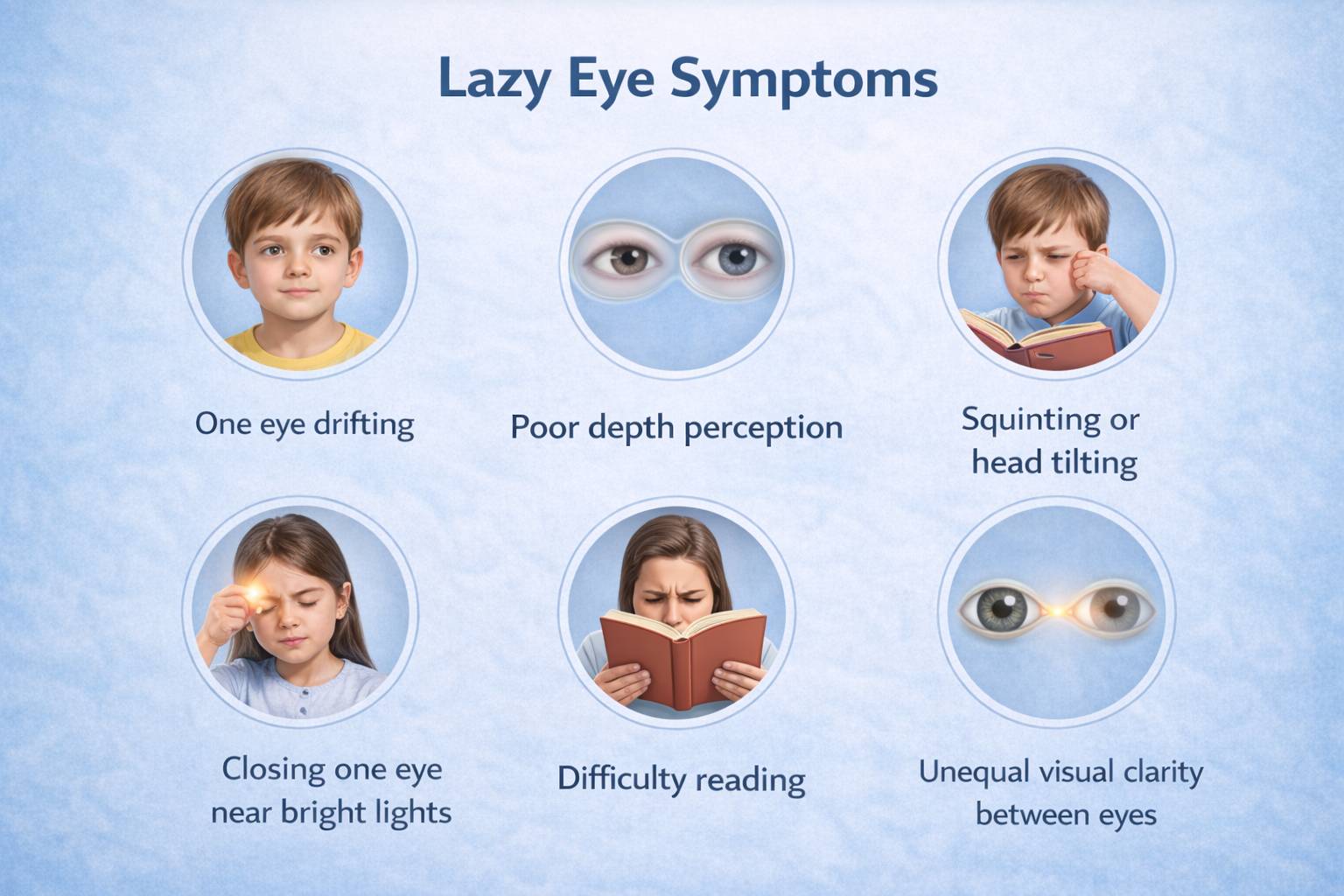
Lazy Eye Symptoms
Identifying lazy eye symptoms early is very important:
- Poor depth perception
- One eye wandering frequently
- Sometimes squinting or tilting the head
- Trouble with reading
- Closing one eye near bright lights
- Eyes with unequal clarity
For proper evaluation, one must seek consultation with a pediatric ophthalmologist or squint specialist.
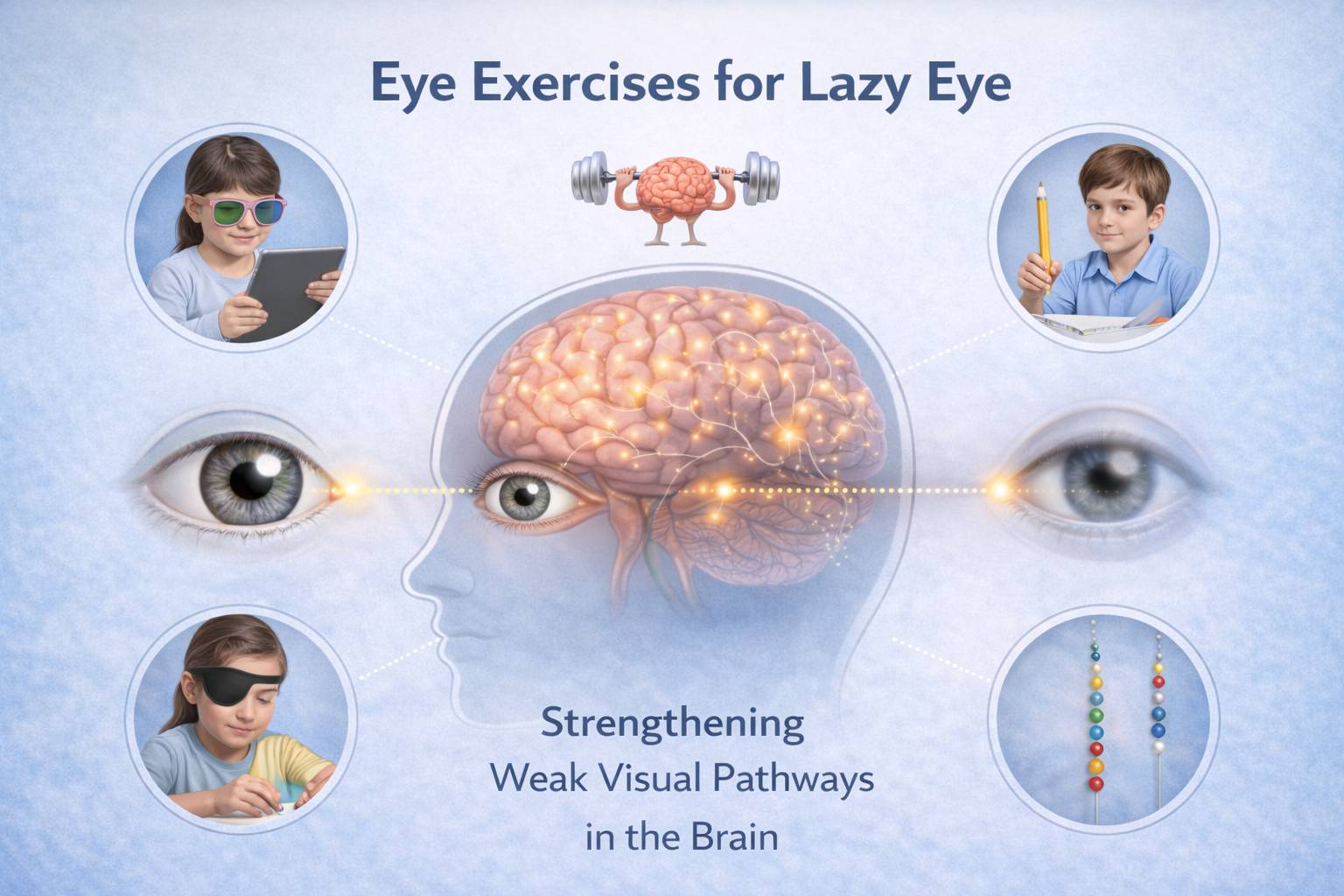
Eye Exercises and Lazy Eye
To strengthen weak visual pathways within the brain, one must undergo various eye exercises. While this is a controversial approach, more and more doctors have begun to utilise supervised programs. Lazy eye treatment exercises work on multiple levels, with the main ones being:
- Age of the patient
- Severity of the amblyopia
- Cause of amblyopia
- Treatment consistency
- Type of exercises
Eye exercises should be performed by children with amblyopia. This is because children have greater neuroplasticity in the brain. However, this approach is not limited to children, and adults with amblyopia can benefit from a structured plan as well because the visual pathways are also somewhat plastic later in life.
Doctor-Approved Eye Exercises for Lazy Eye
1. Patch Therapy Combined with Exercises
Covering the stronger eye strategically teaches the brain to utilize the weaker eye. The integration of amblyopia exercises, such as drawing, coloring, reading, or tracing, yields more significant results.
2. Pencil Push-Ups
Pencil push-ups are primarily prescribed for convergence issues but are also useful for amblyopia, particularly when the weaker eye has difficulty focusing.
How to do it: Keep a pencil at arm's length, maintain focus on the tip, and gradually move it toward your nose while staying focused.
3. Brock String Exercise
The Brock String is a well-known vision therapy exercise for a lazy eye and for strengthening binocular vision.
Patients focus on colored beads while pulling a string, which trains each eye to work together.
4. Visual Tracking Exercises
Enhancing eye coordination, primarily for kids, is the purpose of eye exercises such as tracing shapes, following moving objects, or playing with laser pointer games.
5. Anaglyph (Red-Green) Glasses Therapy
Patients use digital apps or printed worksheets for activities that require the use of both eyes. They undergo tasks that mandate vision cooperation. This is among the best eye exercises to improve vision in amblyopia.
6. Near–Far Focus Switching
This eye exercise to improve vision offers the brain vision access that enhances flexibility while focusing. Patients switch attention from near to far targets and vice versa.
7. Vision Therapy Programs on Computers
Measurable progress is shown with current digital therapies that activate specific pathways within the brain. These are often utilised for the rehabilitation of amblyopia in both paediatrics and adults.
Lazy Eye Activity in Adults: Is It Useful?
It is often believed that amblyopia/all forms of lazy eye is something that cannot be helped/treated beyond childhood. This is false. Although the process is slower, with dedication, adults are definitely still able to make progress with the right effort and intensive therapy.
Using lazy eye activities for adults, such as contrast video games, activities that promote stereopsis, or a combination of a patch and other activities, are excellent for breaking through the neural pathways that have been suppressed. Supervised treatment plans provide optimal results.
Lazy Eye Treatment in Children
Children are also greatly helped with vision therapies, and this is because their visual systems are still growing and developing, making them more adaptable. Entertaining activities that are often used with children include:
- Games that require matching
- Dot-to-dot activities
- Colouring within specific shapes
- Tracing mazes
- Tasks that require 3D vision
- Activities that promote hand-eye coordination
Lazy eye treatment exercises will go unfinished or be ineffective unless there is adult supervision during the activities and during follow-ups.
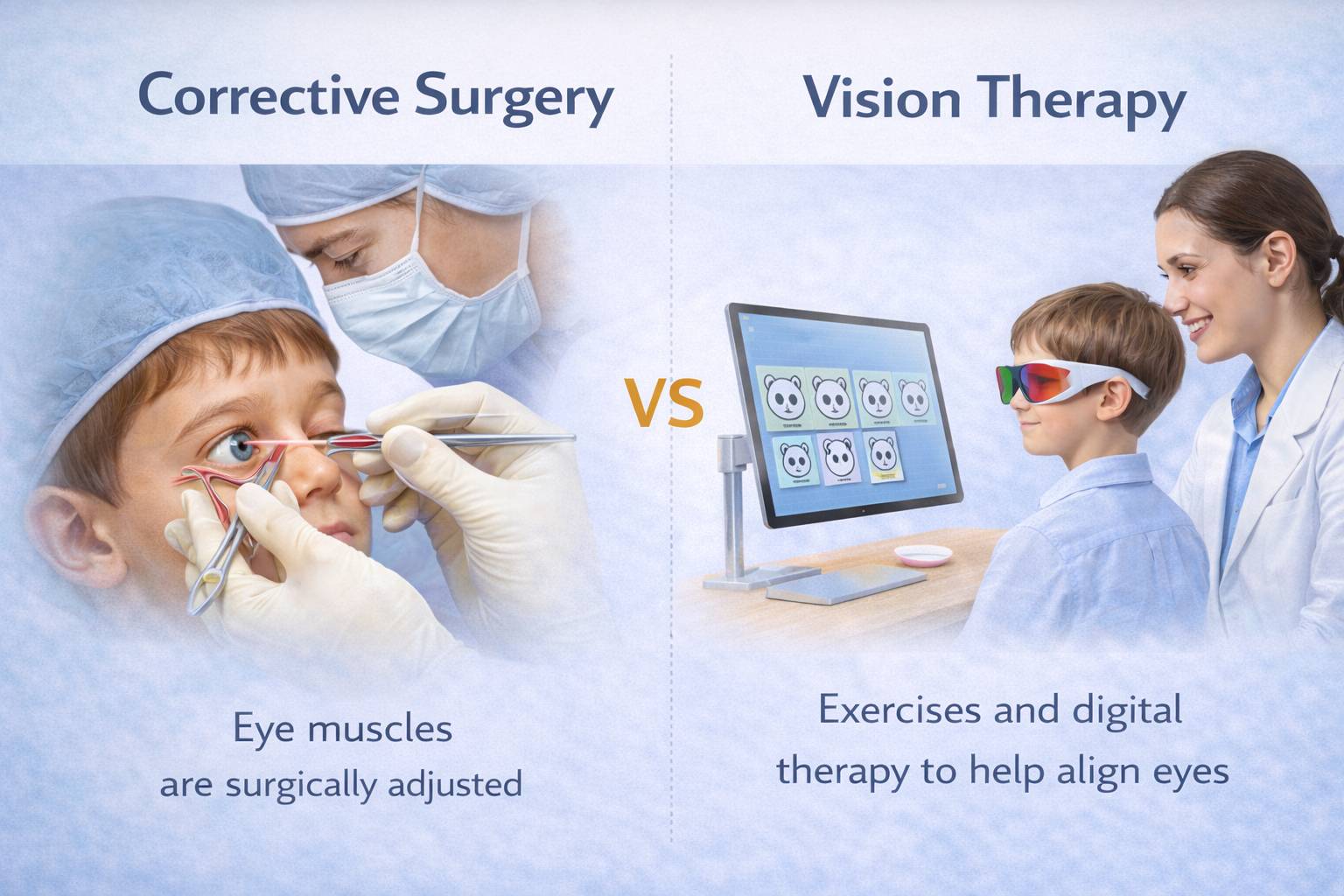
Difference Between Eye Exercises and Vision Therapy
While simple home exercises are helpful, they are not the complete treatment. Components of vision therapy include:
- Creating personalised exercise schedules
- Use of specialised tools
- Sessions conducted under supervision
- Learning new techniques
- Adjusting the eye position
- Advanced techniques for assessing changes
A professional therapy program from an ophthalmologist will give better and more lasting results than doing an exercise program at home.
A Quick Comparison of Eye Exercises and Vision Therapy
| Aspect | Eye Exercises | Vision Therapy |
| Definition | Simple visual activities performed at home to stimulate the weaker eye | A structured, medically supervised rehabilitation program for visual disorders |
| Level of Supervision | Usually self-guided or parent-guided | Supervised by an ophthalmologist or trained vision therapist |
| Personalisation | General exercises with limited customization | Fully personalized based on diagnosis, age, and severity |
| Diagnostic Basis | Often done without detailed clinical assessment | Based on comprehensive eye exams and binocular vision testing |
| Tools Used | Pencils, charts, basic worksheets, apps | Specialized clinical tools, digital therapy systems, prisms, lenses |
| Treatment Scope | Mild amblyopia or supportive therapy | Mild to severe amblyopia, binocular dysfunction, strabismus |
| Effectiveness | Helpful for early or mild cases when done consistently | Proven higher success rate with long-term and measurable outcomes |
| Monitoring Progress | Limited or no objective tracking | Regular progress evaluation and therapy adjustment |
| Risk Factors | Improper use may delay correct treatment | Safe when professionally supervised |
| Time Commitment | Short daily sessions | Scheduled clinical sessions + guided home practice |
| Outcome Stability | Higher risk of relapse if unsupervised | More stable and sustained visual improvement |
| Recommended For | Initial support or maintenance therapy | Comprehensive lazy eye treatment and complex cases |
While eye exercises can support lazy eye improvement, vision therapy provides a complete, medically guided solution with stronger and longer-lasting results.
When Eye Exercises Are Not Enough, Do More Than Eye Exercises
A lazy eye may be more challenging to adjust to than doing the response to accommodation:
- Young children with more severe deprivation amblyopia
- Large eye misalignment
- Presence of cataracts or ptosis
- Underlying uncorrected refractive error
More than exercise therapy may be indicated in these instances.
Importance of Squint Specialists in Managing Lazy Eye
- A squint specialist must evaluate these problems in detail to provide a proper exercise plan along with glasses, patching, or surgery, for the best post-exercise lazy eye outcomes.
- A squint specialist must exercise caution when assessing lazy eye due to strabismus to ensure exercises don’t unintentionally lead to greater misalignment of the eyes.
About Dr. Digvijay Singh
Dr. Digvijay Singh is a renowned pediatric ophthalmologist and squint specialist known for his expertise in treating complex vision disorders, including amblyopia. His patient-focused approach, scientifically designed vision therapy exercises for lazy eye, and advanced diagnostic technologies ensure precise and effective treatment for children and adults. Patients seeking structured therapy, personalised exercise plans, and long-term improvement often rely on his evidence-based care to achieve stronger, healthier vision.
Also Read: What Is Glaucoma? Symptoms, Causes, Treatment & Prevention
Conclusion
Lazy eye is a treatable condition. However, to get the most positive outcomes, it requires the proper therapy techniques. One of the most critical factors of therapy is proper lazy eye diagnosis. To achieve successful outcomes, participants require proper guidance to execute eye controlled lazy eye exercises. Also, structured vision therapy exercises can lead to amazing outcomes; especially for children. With persistent effort, adults can also achieve lazy eye vision exercises and get valuable improvement.
Whether patients rely on at-home lazy exercises, digital lazy eye therapy, or clinical lazy eye therapy, patients can gain greater amblyopia outcomes with therapy. Consultation with a trained ophthalmologist or squint specialist ensures that the patient receives the most appropriate, effective treatment plan tailored to their needs. Contact us for more information on treatment proceedings.
FAQs: Eye Exercises For Lazy Eye
Q.1 Can eye exercises completely cure lazy eye in adults?
Ans. Improvement is possible, but a complete cure is not guaranteed. Adults still have some level of neuroplasticity, meaning the brain can relearn visual skills. With consistent lazy eye exercises for adults, supervised vision therapy, and proper diagnosis, many adults experience better clarity, depth perception, and eye coordination. However, results depend on the severity, age, and underlying cause of amblyopia.
Q.2 How long does it take for kids to show improvement with lazy eye exercises?
Ans. Most children begin to show improvement within 4–12 weeks of consistent eye exercises for lazy eye in children, especially when combined with patching or glasses. Younger children often progress faster because their visual system is still developing. Regular follow-ups with a pediatric ophthalmologist or squint specialist help track progress and adjust treatment.
Q.3 Are home eye exercises enough to treat lazy eye?
Ans. Home exercises can help strengthen the weaker eye, but they may not be sufficient for moderate or severe amblyopia. Full improvement typically requires a structured treatment plan including glasses, patching, and supervised vision therapy exercises for lazy eye. Clinic-based programs provide targeted neurological stimulation that home exercises alone cannot achieve.
Q.4 Can lazy eye return after successful treatment?
Ans. Yes, lazy eye can recur in some cases, especially if treatment stops abruptly or the child is very young. Regular monitoring, follow-up visits, and continued reinforcement through simple amblyopia exercises help maintain vision gains. Children who outgrow amblyopia should have at least annual eye checkups to prevent relapse.
Q.5 Are lazy eye exercises safe for all age groups?
Ans. Yes, lazy eye treatment exercises are safe for children, teens, and adults when recommended by an ophthalmologist. They involve visual tasks that retrain the brain and don’t cause harm. However, if the patient has untreated strabismus, cataract, or severe refractive error, these conditions must be addressed first to avoid worsening the imbalance.





![DigvijayProfile[1]](https://drdigvijaysingh.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/DigvijayProfile1.jpg)

Recent Comments