What is a coloboma?
Coloboma is an eye abnormality that occurs due to maldevelopment of the eye in the fetus. Colobomas are missing pieces of tissue in structures that form the eye and may appear as notches or gaps in one of several parts of the eye. Commonly they are seen in the iris (colored part of the eye), retina (specialized light-sensitive tissue that lines the back of the eye) and choroid (the blood vessel layer under the retina). It may be present in one or both eyes.
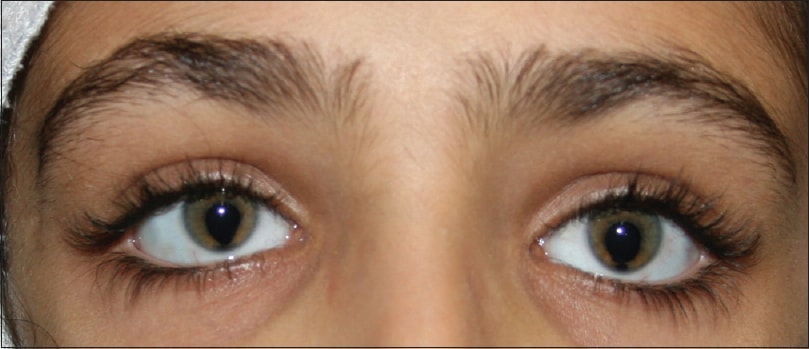
Iris coloboma
What problems do colobomas cause?
Colobomas cause decreased vision and squint if they affect the central part of the retina. In the iris, they cause a keyhole appearance but do not lead to vision loss. Sometimes colobomas are associated with other eye abnormalities such as microphthalmos (developmentally small abnormal eye), cataract, glaucoma and retinal detachments. Eyes with colobomas are at a higher risk for retinal detachment.
What are the types of colobomas?
Different types of coloboma occur in the eye depending on the location affected. They could be eyelid coloboma, iris coloboma, lens coloboma, chorio-retinal coloboma, optic nerve coloboma and uveal coloboma.
What is the treatment for a coloboma?
Unfortunately, treatment option to correct a coloboma are limited and actually deal with the complications of coloboma such as cataract, glaucoma and retinal detachment rather than the defect itself. In iris coloboma and lens coloboma, no treatment is usually needed. In uveal and retino-choroidal coloboma, a laser of the retina is done around the coloboma boundary to reduce the risk of retinal detcahment. Visual rehabilitation and cosmetic squint surgery may be needed in eyes with poor vision.
![DigvijayProfile[1]](https://drdigvijaysingh.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/DigvijayProfile1.jpg)
