What is retinoblastoma?
Retinoblastoma refers to a rare childhood cancer which originates in the retina. Most often, retinoblastoma is unilateral (occurring in one eye) though in about 30% cases it may be bilateral (in both eyes). In the early stages, it is localized within the eyeball but over time it can spread to the lymph nodes, bones, bone marrow and central nervous system (brain and spinal cord).
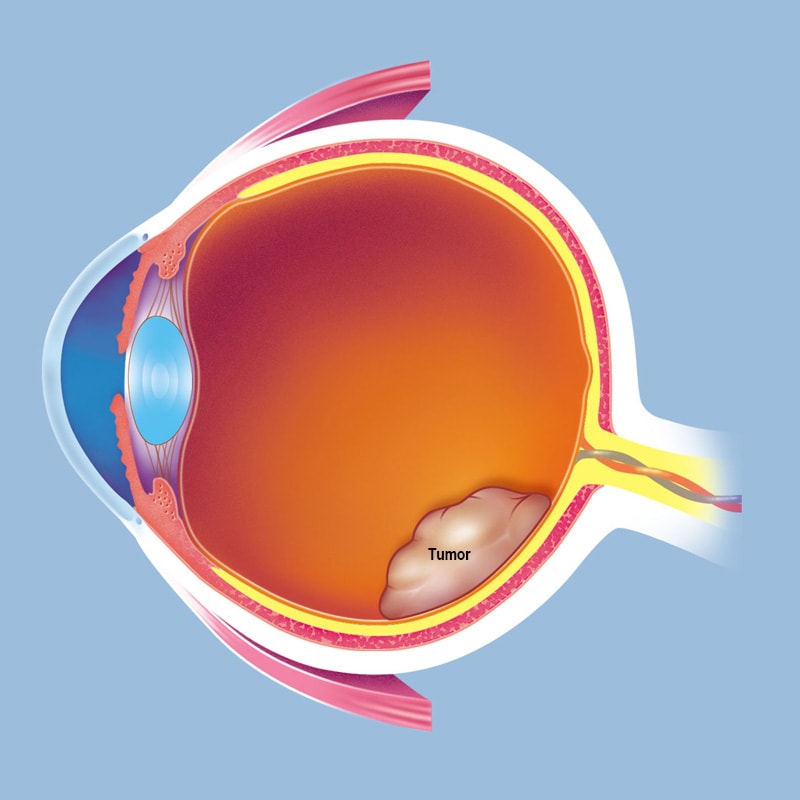
Retinoblastoma tumor mass seen in a fundus photograph
When does retinoblastoma develop?
Children may be born with retinoblastoma, but the disease is rarely diagnosed at birth. Generally in bilateral cases, the disease is identified earlier than unilateral cases.
Can retinoblastoma be cured?
Most children who begin treatment before the retinoblastoma has spread beyond the eye are cured. Unfortunately in developing countries like India, it is diagnosed late and has a high chance of fatality.
Is retinoblastoma inherited?
Retinoblastoma has a genetic locus and it's possible for children to inherit a genetic mutation from their parents. However, most new cases of retinoblastoma have no family history.
How does a child with retinoblastoma present?
Retinoblastoma is generally seen in children less than 5 years of age. Children with retinoblastoma may present with leukocoria (whitish appearance inside the eye), squint and eyelid swelling. Diagnosis is confirmed by an ophthalmologist after doing a dilated eye examination and spotting gray-white tumours with foci of chalky-colored calcification. Ancillary studies that may provide diagnostic help are ultrasonography, MRI and CT.
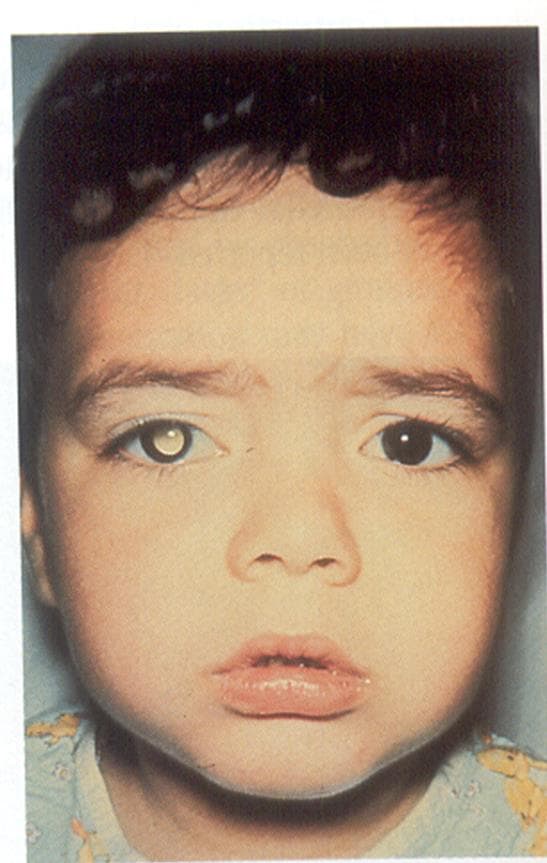
White Reflex (Leukocoria) in the Right eye of a Child with Retinoblastoma
What is the treatment of retinoblastoma?
Tumors in adbaced stages are managed by enucleation (removal of the eyeball). After enuclaetion, an implant is placed in the orbit to provide a good cosmetic appearance with limited to good motility. Recently, with earlier diagnosis and improvements in conservative methods of management such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy, more eyes are being preserved and enucleation rate is reducing. Other forms of treatment include thermotherapy, episcleral plaque brachytherapy, laser photocoagulation, or cryotherapy. The management of retinoblastoma is complex and requires knowledge and experience. Since treatment varies depending on number, size, and location of the tumors, each case must be individualized.
![DigvijayProfile[1]](https://drdigvijaysingh.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/DigvijayProfile1.jpg)
